Stern
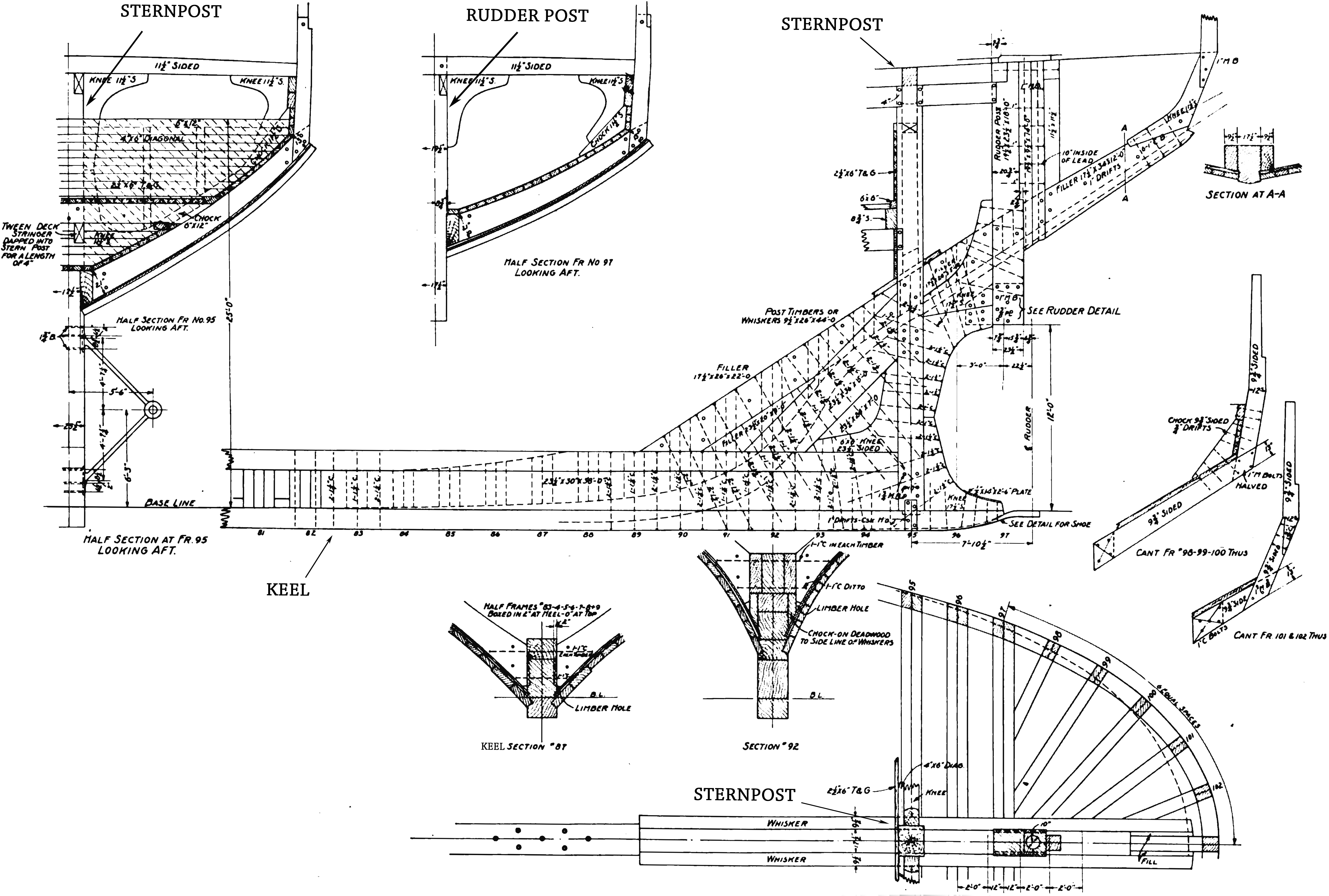 The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night.
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night.Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is designed to support the various beams that make up the stern.
In 1817 the British naval architect Sir Robert Seppings introduced the concept of a rounded stern. The square stern had been an easy target for enemy cannon, and could not support the weight of heavy stern chase guns. But Seppings' design left the rudder head exposed, and was regarded by many as simply ugly—no American warships were designed with such sterns, and the round stern was quickly superseded by the elliptical stern. The United States began building the first elliptical stern warship in 1820, a decade before the British. became the first sailing ship to sport such a stern. Though a great improvement over the transom stern in terms of its vulnerability to attack when under fire, elliptical sterns still had obvious weaknesses which the next major stern development—the iron-hulled cruiser stern—addressed far better and with significantly different materials. Provided by Wikipedia
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
-
17
-
18
-
19
-
20